Blockchain in Modern Finance
- August 28, 2024
- Views 282
Revolutionizing the Future of Transactions
Blockchain technology has rapidly evolved from a niche innovation associated primarily with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to a powerful tool poised to revolutionize the entire financial sector. As a decentralized, transparent, and secure method of recording transactions, blockchain is reshaping how we think about finance, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, security, and inclusivity.
In this blog, we will explore the role of blockchain in modern finance, discussing its potential to transform financial services, the benefits it brings, the challenges it faces, and what the future might hold.
1. Understanding Blockchain Technology
Before diving into its role in finance, it’s important to understand what blockchain technology is and how it works.
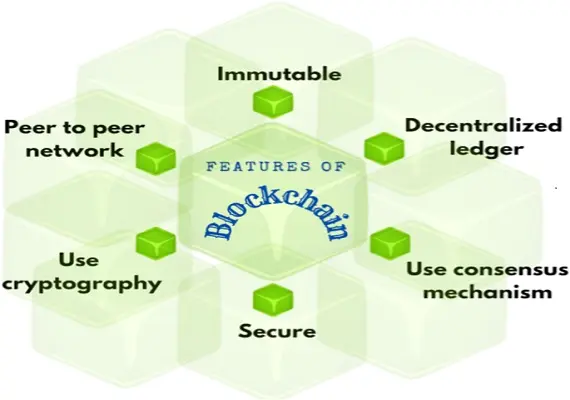
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions across a network of computers in a way that ensures the data is secure, transparent, and immutable. Each transaction is recorded in a "block," and these blocks are linked together in a "chain," hence the term "blockchain."
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases that are typically controlled by a central entity, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, meaning no single party has control over the entire network.
- Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain are visible to participants within the network, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data, making it extremely difficult to alter or hack.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the ledger.
These features make blockchain an attractive technology for modern finance, where security, transparency, and trust are paramount.
2. Blockchain's Impact on Financial Services
Blockchain's unique attributes are driving significant changes in various aspects of financial services, from payments and remittances to capital markets and beyond.
a. Payments and Remittances
One of the most prominent applications of blockchain in finance is in payments and remittances. Traditional cross-border payments can be slow, expensive, and opaque, often taking days to settle with high fees due to the involvement of multiple intermediaries.
Blockchain’s Impact:
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain enables near-instantaneous cross-border transactions, reducing settlement times from days to minutes or even seconds.
- Lower Costs: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain reduces transaction fees, making remittances more affordable, particularly for those in developing countries.
- Increased Transparency: Every transaction on a blockchain is recorded and visible to all parties involved, reducing the risk of fraud and improving transparency.
Example: Ripple's XRP Ledger is a notable example, offering a blockchain-based solution for cross-border payments that is faster and cheaper than traditional systems.
b. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute transactions when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Blockchain’s Impact:
- Automation and Efficiency: Smart contracts streamline processes like loan disbursements, insurance claims, and trade finance by automating them, reducing the time and costs associated with manual processing.
- Security and Trust: Since smart contracts run on blockchain, they are secure and immutable, ensuring that the agreed-upon conditions are met without the need for third-party verification.
Example: Ethereum is the most widely used blockchain platform for smart contracts, supporting a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) in finance.
c. Capital Markets
Blockchain technology is also making inroads into capital markets, offering the potential to revolutionize the trading, settlement, and management of assets.
Blockchain’s Impact:
- Tokenization of Assets: Blockchain enables the tokenization of assets, where real-world assets like stocks, bonds, real estate, or even art can be represented as digital tokens on a blockchain. This makes it easier to trade, divide, and transfer ownership of these assets.
- Faster Settlement: Traditional securities trading often involves a lengthy settlement process. Blockchain can enable real-time or near-real-time settlement, reducing counterparty risk and increasing liquidity.
- Improved Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of all transactions, which can improve regulatory compliance and reduce the risk of fraud.
Example: The Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) is developing a blockchain-based platform to replace its current settlement system, aiming to improve efficiency and transparency.
d. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
One of the most transformative impacts of blockchain on modern finance is the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi refers to a broad range of financial applications built on blockchain that aim to recreate and improve traditional financial systems in a decentralized, permissionless, and open manner.
Blockchain’s Impact:
- Peer-to-Peer Lending and Borrowing: DeFi platforms enable individuals to lend and borrow assets directly from one another without intermediaries, often at more competitive rates than traditional banks.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies and other assets directly with each other, without relying on a centralized exchange. This reduces the risk of exchange hacks and gives users more control over their funds.
- Yield Farming and Staking: DeFi offers new ways for users to earn returns on their assets through activities like yield farming (providing liquidity to DeFi platforms) and staking (participating in the validation of transactions on proof-of-stake blockchains).
Example: Uniswap is a popular decentralized exchange that allows users to trade tokens directly from their wallets without needing to trust a centralized entity.
3. Benefits of Blockchain in Finance
Blockchain’s integration into the financial sector offers numerous benefits, which are driving its adoption across the industry.
a. Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s cryptographic nature makes it inherently secure. Transactions are encrypted and linked to previous transactions, making unauthorized changes extremely difficult. This reduces the risk of fraud, hacking, and data breaches.
b. Greater Transparency
All transactions on a blockchain are recorded in a public or private ledger that is accessible to all network participants. This transparency reduces the risk of corruption, fraud, and mismanagement, as every transaction can be audited and verified.
c. Improved Efficiency
By automating processes and eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain significantly improves the efficiency of financial transactions. This not only speeds up transactions but also reduces operational costs, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
d. Financial Inclusion
Blockchain has the potential to bring financial services to millions of unbanked or underbanked individuals around the world. With blockchain, people can access financial services using just a smartphone, bypassing the need for traditional banking infrastructure.
4. Challenges Facing Blockchain Adoption in Finance
While the potential of blockchain in finance is immense, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
a. Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the biggest challenges is the lack of clear and consistent regulatory frameworks for blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Different countries have different approaches to regulation, leading to uncertainty for businesses and consumers.
b. Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks can struggle with scalability, especially when processing a large number of transactions. This can lead to slower transaction times and higher fees, which are barriers to widespread adoption in finance.
c. Interoperability
With multiple blockchain platforms in existence, interoperability—or the ability for different blockchains to communicate and work together—is a significant challenge. For blockchain to reach its full potential in finance, these systems must be able to interact seamlessly.
d. Adoption and Integration
Integrating blockchain with existing financial systems and infrastructure is complex and can be costly. There is also resistance to change from established financial institutions, which may be hesitant to adopt new technologies that could disrupt their business models.
5. The Future of Blockchain in Finance
Despite the challenges, the future of blockchain in finance looks promising. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks become clearer, we can expect to see even greater adoption across the financial sector.
a. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Many central banks around the world are exploring the issuance of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) using blockchain technology. CBDCs could provide a digital alternative to cash, improving the efficiency of payments and financial inclusion.
b. Expanded Use Cases
As blockchain technology evolves, new use cases will emerge in areas like trade finance, supply chain management, and insurance. These applications have the potential to further disrupt and enhance the financial services industry.
c. Greater Collaboration Between Traditional Finance and DeFi
We are likely to see increased collaboration between traditional financial institutions and DeFi platforms. This could lead to a hybrid financial system that leverages the strengths of both centralized and decentralized finance.
Conclusion
Blockchain is no longer just a buzzword—it's a transformative technology that is reshaping the financial industry. By enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency, blockchain is helping to create a more inclusive and robust financial system.
However, for blockchain to realize its full potential in modern finance, challenges such as regulatory uncertainty, scalability, and interoperability must be addressed. As these hurdles are overcome, we can expect blockchain to play an increasingly central role in the future of finance, revolutionizing how transactions are conducted, assets are managed, and financial services are delivered.